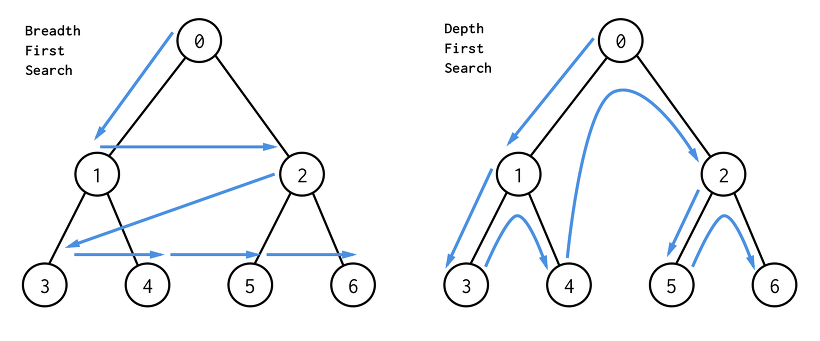
DFS(Depth First Search)
- 루트 노드(최상단 혹은 다른 임의의 노드)에서 최대한 깊이 내려간 뒤 더 이상 깊이 갈 곳이 없을 경우 옆으로 이동하는 탐색 방법입니다.
- 모든 노드를 방문하고자 하는 경우 선택(완전 탐색)한다.
- 비교적 간단하나 검색 속도 자체는 너비 우선 탐색에 비해 느리다.
-
스택 또는 재귀 함수로 구현한다.
-
예시 : DFS는 게임에서 적을 상대할 때 한 부분만 다 때리고 다른 부분으로 넘어가 타격하는 느낌이다.
BFS(Breadth First Search)
- 루트 노드(최상단 혹은 다른 임의의 노드)에서 가까운 노드부터 방문하고 멀리 떨어져 있는 정점을 나중에 순차적으로 방문하는 탐색 방법입니다.
- 주로 노드 사이의 최단 경로를 찾고 싶을 때 이 방법을 사용한다.
- 큐를 이용해서 구현한다.
- 예시 : BFS는 게임에서 적을 상대할 때 여러 군데를 골고루 때리며 조금씩 쓰러뜨리는 느낌이다.
Java 구현
DFS 재귀
class DFS {
boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] array = { {1,2}, {0,3,4}, {0,5,6}, {1}, {1}, {2}, {2} };
visited = new boolean[array.length]
dfs(0);
}
public void dfs(int start){
visited[start] = true; //방문처리
System.out.println(start); //방문했으면 값 출력
for(int next : array[start]){ //
if(!visited[next]){ //반복하지 않은 노드에서 재귀 호출
dfs(next);
}
}
}
}
- 위 list는 위 그림에서 해당 인덱스에 연결된 노드를 정렬한 것이다.
- 0은 1, 2 노드와 연결되어 있다.
DFS 스택
class DFS {
boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] array = { {1,2}, {0,3,4}, {0,5,6}, {1}, {1}, {2}, {2} };
visited = new boolean[array.length]
dfs(0);
}
public void dfs(int start){
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); //스택 생성
stack.push(start); //스택에 첫 번째 인덱스 삽입
while (!stack.isEmpty()){ //스택에 뭔가 있다면
int now = stack.pop(); //꺼내고
if (!visited[now]){ //방문하지 않았다면
visited[now] = true; //방문 처리
System.out.println(now); //방문했으면 값 출력
for (int i = 0; i < array[now].length; i++){
int next = array[now][i]; //해당 리스트를 순회하며
if (!visited[next]){
stack.push(next); //방문하지 않은 값을 스택에 넣는다.
}
}
}
}
}
}
BFS
class BFS{
boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] array = { {1,2}, {0,3,4}, {0,5,6}, {1}, {1}, {2}, {2} };
visited = new boolean[array.length]
bfs(0);
}
public void bfs(int start){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // 큐 생성
queue.add(start); //시작 값을 넣는다.
visited[start]=true; //방문 처리
while(!queue.isEmpty()){ //큐에 뭔가 있다면
int now = queue.poll(); //큐에서 값을 빼고
System.out.println(now); //방문 출력
for(int next :array[now]){ 해당 방문 리스트 순회
if(!visited[next]){
queue.add(next); //방문하지 않으면 큐에 삽입
visited[next]=true; //방문 처리
}
}
}
}
DFS, BFS를 활용한 문제 유형
- 그래프의 모든 정점을 방문하는 것이 중요할 때는 둘 중에 편한 것을 사용한다.
- 경로의 특성이 저장해야 할 때는 DFS, BFS는 경로의 특성을 가지지 못한다.
- 최단 거리를 구할 때는 BFS를 사용한다. 노드에서 가까운 곳부터 찾기 때문에 경로 탐색시 먼저 찾아지는 것이 최단 거리이다.
실전 프로그래머스 문제 예시
DFS
- 피로도_프로그래머스
class Solution {
boolean[] visited;
int max=0;
public int solution(int k, int[][] dungeons) {
visited = new boolean[dungeons.length];
dfs(k, dungeons, 0);
return max;
}
//dfs 함수 생성
private void dfs(int tired, int[][] dungeons, int count){
//던전을 돌면서
for(int i =0 ; i<dungeons.length;i++){
//방문하지 않았거나 피로도보다 작다면
if(!visited[i] && dungeons[i][0]<=tired){
visited[i]=true; //방문 처리
dfs(tired-dungeons[i][1], dungeons, count+1); //count 올리고 재귀
visited[i]=false; //다음을 위해 재초기화
}
}
max=Math.max(count, max); //최대값을 구한다.
}
}
BFS
- 전력망 둘로 나누기_프로그래머스
class Solution {
public List<Integer>[] list;
public int solution(int n, int[][] wires) {
int answer = 100;
list = new List[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n ; i++) {
list[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for(int[] wire : wires){
list[wire[0]].add(wire[1]);
list[wire[1]].add(wire[0]);
}
for(int[] wire : wires){
int n1 = bfs(wire[0], wire[1], n); //한쪽 방향
int n2 = bfs(wire[1], wire[0], n); //반대편 방향
answer = Math.min(answer, Math.abs(n1-n2));
}
return answer;
}
//bfs
public int bfs(int v1, int v2, int n){
//큐 생성
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n+1];
int count=0;
queue.add(v1); //큐에 시작 노드 넣어줌
visited[v1] = true; //방문확인
//큐가 빌 때까지 반복
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int now = queue.poll(); //하나를 꺼내고
count++; //횟수를 더한다.
for(int next : list[now]){ //시작점의 리스트를 순회하면서
if(next != v2 && !visited[next]){ //방문하지 않았거나, 간선을 끊어서 처리
queue.add(next);
visited[next]=true;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
Reference:
- Algorithm -알고리즘 그래픽 디자인 img_최형주
- 그래프 탐색 알고리즘 [DFS, BFS] _ 망나
- 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS) 과 너비 우선 탐색(BFS) _ 튜나의 개발일기
- 피로도, 전력망 둘로 나누기_프로그래머스