사이킷런에 구현되어 있는 결정트리관련 클래스
트리노드 클래스 구현
-
클래스의 속성과 메소드
- 결정트리에서의 각 노드는 특성공간 X의 부분집합에 대응하므로 이 부분집합에 속하는 훈련 데이터셋 self.X 와 레이블 self.y가 필요함
- 결정트리에서 노드가 위치하는 깊이:self.depth
- 노드에서 분할규칙 $s_{j}^{x_{ij}}$를 결정하는 속성
self.j와 기준값 $x_{ij}$를 나타내는self.xi - 자식노드:
self.left,self.right - 노드에 대응되는 예측함수:
self.g - 노드에 대응하는 집합 $\mathcal A$에서의 예측함수 $g^{\mathcal A}$를 이용하여 $\mathcal A$에 속하는 훈련샘플에 대한 MSE를 계산하는 함수
CalculateLoss
#트리노드 클래스
import numpy as np
class TNode:
def __init__(self, depth, X, y):
self.depth = depth #트리노트 깊이
self.X = X # 특성벡터의 행렬
self.y = y # 레이블 벡터
# 분할규칙 파라미터의 초기화
self.j = None
self.xi = None
# 자식노드 초기화
self.left = None
self.right = None
# 노드에 대응되는 영역 A에서 정의된 예측함수 g 초기화
self.g = None
def CalculateLoss(self):
if (len(self.y)==0):
return 0
return np.sum(np.power(self.y-self.y.mean(), 2)) #예측값을 빼서 제곱한 값의 합
결정트리 학습 알고리즘 Construct_Subtree
def Construct_Subtree(node, max_depth):
if (node.depth == max_depth or len(node.y) == 1):
node.g = node.y.mean()
# 미리 설정된 깊이에 도달, 더 이상 분할할 수 없을 때 리프노드에 대한 예측 함수를 설정
else:
j, xi = CalculateOptimalSplit(node) # 손실값이 최소가 되는 규칙을 찾아 j,xi를 반환(아래에 있음)
node.j = j
node.xi = xi
Xt, yt, Xf, yf = DataSplit(node.X, node.y, j, xi) # Xt,yt,Xf,yf 나누기
if (len(yt)>0):
node.left = TNode(node.depth +1 , Xt, yt)
Construct_Subtree(node.left, max_depth)
if (len(yf)>0):
node.right = TNode(node.depth +1, Xf, yf)
Construct_Subtree(node.right, max_depth)
return node
# 현재의 자식노드 설정, Construct_Subtree 재귀적으로 사용하여 트리구조 구현
def DataSplit(X, y, j, xi):
#CalculateOptimalSplit함수를 이용하여 구한 분할규칙에 따라 A의 분할 A_T, A_F에 대응되는 노드를 생성하기 위해, 현재 노드에 대응되는 영역 A에 속하는 훈련 데이터셋 X,y를 영역 A_T에 속하는 훈련 데이터셋 Xt, yt와 영역 A_F에 속하는 훈련 데이터셋 Xf, yf로 나누어주는 함수 DataSplit를 별도로 구현
ids = X[:, j]<= xi
Xt = X[ids == True, :]
Xf = X[ids == False, :]
yt = y[ids == True]
yf = y[ids == False]
return Xt, yt, Xf, yf
def CalculateOptimalSplit(node): #주어진 노드에 대응되는 영역을 분할, 훈련데이터셋에 손실값이 최소가 되는 규칙을 찾아 j,xi를 반환해주는 함수 구현
X = node.X
y = node.y
best_feature = 0
bext_xi = X[0, best_feature]
best_split_val = node.CalculateLoss()
m,n = X.shape
for j in range(0,n):
for i in range(0,m):
xi = X[i,j]
Xt, yt, Xf, yf = DataSplit(X,y,j,xi)
tmpt = TNode(0, Xt, yt)
tmpf = TNode(0, Xf, yf)
loss_t = tmpt.CalculateLoss()
loss_f = tmpf.CalculateLoss()
curr_val = loss_t + loss_f
if (curr_val < best_split_val):
best_split_val = curr_val
best_feature = j
best_xi = xi
return best_feature, best_xi
예측기 구현: 예측기 Predict를 재귀적으로 구현
def Predict(X, node):
if (node.right == None and node.left != None): #오른쪽에 없고 왼쪽에 있으면 왼쪽으로 간다.
return Predict(X, node.left)
if (node.right != None and node.left == None): #오른쪽에 있고, 왼쪽에 없으면 오른쪽으로 간다.
return Predict(X, node.right)
if (node.right == None and node.left == None): #오른쪽, 왼쪽 둘 다 없으면 값 예측함수 반환
return node.g
else: #둘 다 값이 존재하면
if (X[node.j] <= node.xi): #분할규칙보다 작거나 같으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽
return Predict(X, node.left)
else:
return Predict(X, node.right)
실습 데이터셋 생성 및 결정트리 실습
from sklearn.datasets import make_friedman1
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
def makedata():
n_samples = 500
X, y = make_friedman1(n_samples = n_samples, n_features = 5, noise=1.0, random_state=100)
return train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=3)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = makedata()
# 결정트리 깊이 설정
max_depth = 10
# depth 0에서 루트노드 생성
treeRoot = TNode(0, X_train, y_train)
# 결정트리 학습
Construct_Subtree(treeRoot, max_depth)
#예측
y_hat = np.zeros(len(X_test))
for i in range(len(X_test)):
y_hat[i] = Predict(X_test[i], treeRoot)
MSE = np.mean(np.power(y_hat - y_test,2))
print("직접 구현한 결정트리: loss=", MSE)
#직접 구현한 결정트리: loss= 9.067077996170276
sklearn.tree 모듈의 DecisionTreeRegressor와 비교
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
regTree = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth = 10, random_state=0)
regTree.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_hat2 = regTree.predict(X_test)
MSE2 = np.mean(np.power(y_hat2-y_test, 2))
print("직접 구현한 결정트리: loss=", MSE)
print("사이킷런 결정트리: loss=", MSE2)
#직접 구현한 결정트리: loss= 9.067077996170276
#사이킷런 결정트리: loss= 10.197991295531748
sklearn의 분류문제에 대한 결정트리 구현
-
sklearn.tree모듈의DecisionTreeClassifier클래스를 이용하여 분류기 객체를 생성할 때 사용되는 변수 중 몇 가지criterion변수: 학습시킬 때 사용할 불순도를 설정하는 변수로 기본값은criterion="gini","entropy"를 선택하면 엔트로피 불순도random_state변수: 결정트리를 학습시키는 과정에서 분할을 하는 매 단계마다 특성의 순서를 랜덤하게 섞게 되는데, 이때 사용되는 랜덤함수의 초깃값을 설정하는 변수max_features변수: 분할하는 매 단계에서 새롭게 순서가 정해진 특성에 대해 처음max_features개의 특성만을 선택하도록 정하는 변수
Moon 데이터셋을 분류하기 위해 여러 가지 규제를 통해 좋은 결정트리 분류기를 만드는 실습
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
# 데이터셋 생성
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=10000, noise=0.3, random_state=42)
# 훈련 데이터셋과 검증 데이터셋으로 나누기
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 결정경계 그림을 그리는 함수
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_boundary(clf, X, y, axes=[0, 7.5, 0, 3], legend=False):
x1s = np.linspace(axes[0], axes[1], 100)
x2s = np.linspace(axes[2], axes[3], 100)
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(x1s, x2s)
X_new = np.column_stack([x1.ravel(), x2.ravel()])
y_pred = clf.predict(X_new).reshape(x1.shape)
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#fafab0','#9898ff','#a0faa0'])
plt.contourf(x1, x2, y_pred, alpha=0.3, cmap=custom_cmap)
custom_cmap2 = ListedColormap(['#7d7d58','#4c4c7f','#507d50'])
plt.contour(x1, x2, y_pred, cmap=custom_cmap2, alpha=0.4)
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1], c='g', marker='o', s= 5, alpha=0.4)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1], c='y', marker='s', s= 5, alpha=0.4)
plt.xlabel(r"$x_1$", fontsize=10)
plt.ylabel(r"$x_2$", fontsize=10, rotation=0)
if legend:
plt.legend(loc="lower right", fontsize=10)
# 규제가 없는 모델과 리프노드가 최소한 4개이상의 샘플을 가져야 한다는 규제조건이 있는 모델의 비교
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
tree_clf1 = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
tree_clf2 = DecisionTreeClassifier(min_samples_leaf=4, random_state=42)
tree_clf1.fit(X_train, y_train)
tree_clf2.fit(X_train, y_train)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(14, 4), sharey=True)
plt.sca(axes[0])
plot_decision_boundary(tree_clf1, X_train, y_train, axes=[-2, 3, -1.5, 2])
plt.title("No restrictions", fontsize=10)
plt.sca(axes[1])
plot_decision_boundary(tree_clf2, X_train, y_train, axes=[-2, 3, -1.5, 2])
plt.title("min_samples_leaf = {}".format(tree_clf2.min_samples_leaf), fontsize=10)
plt.ylabel("")
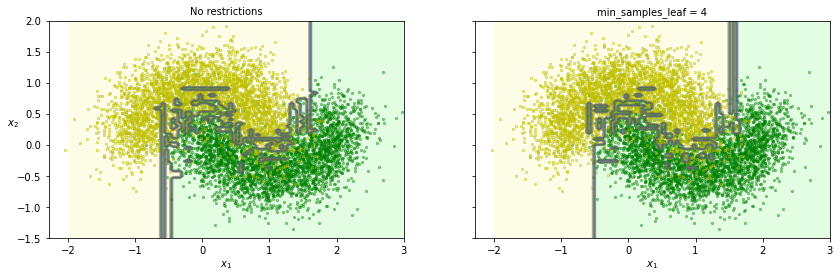
- 확실히 규제가 없을 떄는 과대적합이 일어난다.
# 테스트 데이터셋에 대한 정확도
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
y_pred_t1 = tree_clf1.predict(X_train)
y_pred_t2 = tree_clf2.predict(X_train)
y_pred1 = tree_clf1.predict(X_test)
y_pred2 = tree_clf2.predict(X_test)
print(f"규제가 없는 결정트리 훈련 데이터셋 정확도:{accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_t1)}")
print(f"규제가 있는 결정트리 훈련 데이터셋 정확도:{accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_t2)}\n")
print(f"규제가 없는 결정트리 테스트 데이터셋 정확도:{accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred1)}")
print(f"규제가 있는 결정트리 테스트 데이터셋 정확도:{accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred2)}")
#규제가 없는 결정트리 훈련 데이터셋 정확도:1.0
#규제가 있는 결정트리 훈련 데이터셋 정확도:0.9472857142857143
#규제가 없는 결정트리 테스트 데이터셋 정확도:0.8836666666666667
#규제가 있는 결정트리 테스트 데이터셋 정확도:0.888
GridSearchCV를 이용하여 교차검증으로 적절한 하이퍼파라미터 선택
-
sklearn.model_selection모듈의GridSearchCV클래스 (참고:API) -
GridSearchCV의 객체를 생성할 때cv=k로 설정하면 k겹 교차검증을 통해 좋은 하이퍼파라미터를 선택 -
최종으로 찾은 하이퍼파라미터와 전체 데이터셋을 이용하여 학습한 예측기를 구해줌 : 객체의
best_estimator_속성을 통해 접근- 가장 좋은 하이퍼파라미터는 객체의
best_params_를 통해 접근
- 가장 좋은 하이퍼파라미터는 객체의
# 격자탐색(grid search)를 이용한 교차검증을 통해 규제 파라미터 max_leaf_nodes, min_samples_leaf를 선택
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
params = {'max_leaf_nodes': list(range(2, 100)), 'min_samples_leaf': [2, 3, 4]}
grid_search_cv = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42), params, verbose=1, cv=3, n_jobs=-1)
grid_search_cv.best_params_
#{'max_leaf_nodes': 29, 'min_samples_leaf': 2} 리프 갯수는 29개 최소 리프내 샘플 갯수는 2개했을 때 좋은 결과
best_clf = grid_search_cv.best_estimator_
plot_decision_boundary(best_clf, X_train, y_train, axes=[-2, 3, -1.5, 2])
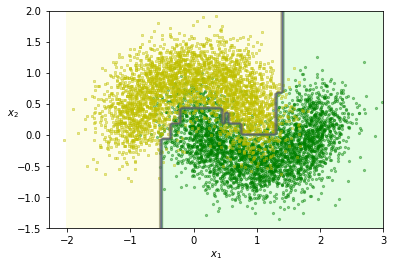
y_pred_t3 = best_clf.predict(X_train)
y_pred3 = best_clf.predict(X_test)
print(f"격자탐색 결정트리 훈련 데이터셋 정확도:{accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_t3)}\n")
print(f"격자탐색 결정트리 테스트 데이터셋 정확도:{accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred3)}")
#격자탐색 결정트리 훈련 데이터셋 정확도:0.9211428571428572
#격자탐색 결정트리 테스트 데이터셋 정확도:0.9156666666666666
과대적합이 많이 없어진 것을 알 수 있다.
Reference:
- 기계학습_하길찬 교수님 수업을 듣고 공부한 내용입니다.