AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming, 관점 지향 프로그래밍)
- AOP는 어디에 관점을 두는가? 로 시작한다.
- 쉽게 말하면 로직을 공통된 로직과 핵심 로직을 나누어 사용하겠다는 것이다.
- 중요한 것은 관심 분리(Separation of Concerns)이다.
-
- 횡단 관심 (Crosscutting Concerns)
- 모든 메소드에 들어있는 공통된 로직을 의미한다.
-
- 핵심 관심 (Core Concerns)
- 각 메소드에만 들어 있는 핵심 관심 코드을 의미한다.
-
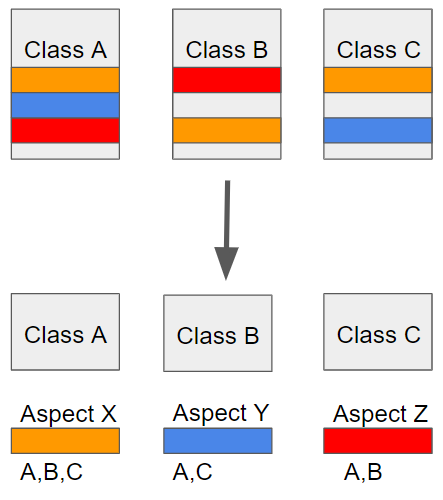
- 위 그림에서 Class A, Class B, Class C가 핵심 관심이다.
- 주황색, 파란색, 빨간색 블럭이 횡단 관심이다.
- 반복되는 횡단 관심을 모듈화를 통해 분리하고 재사용하는 것이다.
AOP가 왜 필요할까?
- 첫 번째 상황 : 비즈니스 메소드 속에는 모든 메소드가 가지고 있는 공통된 코드들과 각각의 메소드만 가지고 있는 핵심 코드가 있다. 공통된 로직을 매 메소드마다 반복하는 것은 유지 보수에 좋지 않다.
- 두 번째 상황 : 모든 비즈니스 메소드의 실행 시간을 확인하거나, 모든 메소드 실행시 매번 log를 콘솔에 출력해야 한다면 모든 메소드에 일일히 해당 코드를 추가 작성하는 일은 어려우며 유지 보수에도 쉽지 않다.
AOP 상세 용어 정리
- JointPoint : Advice가 일어날 수 있는 모든 비즈니스 메소드의 시점을 의미한다.
- Aspect(Advisor) : Pointcut + Advice
- Aspect(Advisor) : Pointcut과 Advice의 결합(모듈화), Pointcut의 시점에 Advice가 실행되는 것을 의미한다.
- Pointcut : 횡단 관심(Advice)이 일어나는 시점을 의미한다. (필터링된 JointPoint)
- Advice : 횡단 관심에 해당하는 실행될 공통 기능의 코드를 의미한다.
AOP 사용 방법
- .xml 파일-Namespaces-
aop사용 체크 (Eclipse 기준) - .xml 작성
<beans> <!--세부 내용 생략 -->
<!--횡단 관심에 해당하는 Advice 클래스 빈 등록-->
<bean id="id" class="클래스 패키지 주소"></bean>
<!--AOP 설정 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="allPointcut" expression="execution(* com.naver.biz..*Service.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="id">
<aop:after pointcut-ref="allPointcut" method="beanMethod"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- aspect에서 pointcut-ref= “allPointcut” 은 포인트 컷이 expression 필터링된 시점이다.
- allPointcut이 실행될 때 ref=”id” 인 bean 클래스의 beanMethod가 Advice로 실행된다.
<aop:after ...>는 동작 시점을 의미하며 before, after, after-returning, after-throwing, around 속성을 사용할 수 있다. (아래에서 더 설명)
pointcut expression 작성법
- Advice가 실행되는 시점을 작성하는 것이다.
- excution() 명시자 내부에 작성한다.
[리턴타입] [패키지 경로][클래스 이름].[메소드 이름 및 매개변수]- 리턴 타입 : 리턴 타입 뒤에 띄어쓰기
*: 모든 리턴을 허용한다.- void : 리턴 타입이 void인 메소드 필터링한다.
- !void : 리턴 타입이 void가 아닌 메소드 필터링한다.
- 패키지 경로
- com.naver.biz.users : 정확한 패키지명으로 필터링한다.
- com.naver.biz.. : com.naver.biz로 시작하는 모든 패키지를 필터링한다.
- com.naver..users : com.naver로 시작하는 패키지 중 패키지 마지막이 user인 패키지를 필터링한다.
- 클래스 이름 : 클래스 이름 뒤에 .
- UserService : UserService 클래스를 필터링한다.
- *Service : 클래스 이름이 Service로 끝나는 클래스를 필터링한다.
- 메소드 이름
- insertUser : insertUser 메소드를 필터링한다.
- insert* : insert로 시작하는 모든 메소드를 필터링한다.
- 매개 변수
- (..) : 모든 경우의 매개변수의 갯수와 타입 허용한다.
- (*) : 매개변수를 1개 받는 메소드를 필터링한다.
- (int, String) : int형, String형을 매개변수로 받는 메소드를 필터링한다.
- 예시
-
expression="execution(void com.naver..*Impl.get*(..))"- 리턴 타입이 void, com.naver.. 아래 모든 클래스 중 클래스 이름이 Impl로, 메소드 이름이 get으로 시작하는 모든 메소드를 필터링한다.
-
expression="execution(* com.kakao.biz.*.*user(*,*))"- com.kakao.biz 아래 모든 클래스, user로 끝나는 메소드이며 매개변수를 2개 받는 메소드를 필터링한다.
-
AOP 동작 시점
- before : 비즈니스 메소드 실행 전 무조건 동작한다.
- after : 비즈니스 메소드 실행 후 무조건 동작한다.
- after-returning : 비즈니스 메소드 실행 후 데이터를 return하고 Advice에서 인자로 받아 사용 가능하다.
- .xml 파일에서 returning 속성으로 리턴할 데이터명을 설정할 수 있다. (유효성 검사에 사용할 수 있다.)
- 비즈니스 메소드의 리턴 타입이 void이면 NullPointerException이 일어나니 주의해야 한다.
- after-throwing : 비즈니스 메소드 실행시 예외 발생시 예외 객체를 return하고 Advice에서 인자로 받아 사용 가능하다.
- .xml 파일에서 throwing 속성으로 리턴할 예외 변수명을 설정할 수 있다.
- after-returning : 비즈니스 메소드 실행 후 데이터를 return하고 Advice에서 인자로 받아 사용 가능하다.
- around : 메소드 호출을 가로채 비즈니스 메소드 전후에 로직을 처리할 수 있다.
- around Advice는 ProceedingJoinPoint 객체를 인자로 받아야 한다.
public Object aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{ String method =jp.getSignature().getName(); Object returnObj =null; System.out.println("비즈니스 메소드 사전처리") returnObj = jp.proceed(); System.out.println("비즈니스 메소드 사후처리") System.out.println(method+ "() 비즈니스 메소드 실행완료"); return returnObj; } - 또한 ProceedingJoinPoint를 통해 메소드의 반환형, 이름, 매개변수 등의 정보를 얻을 수 있으며 around Advice만 ProceedingJoinPoint을 사용한다.
- ProceedingJoinPoint는 around Advice를 위한 preoceed() 메소드가 추가되어있다.
- 나머지 Advice는 ProceedingJoinPoint의 부모인 JoinPoint 객체를 통해 메소드의 반환형, 이름, 매개변수 등의 정보를 얻을 수 있다.
AOP Annotation
- .xml 파일에
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>을 설정해준다.(<aop:config>는 없어도 된다.) - Advice 클래스에
@Service를 붙여 bean 등록을 대체한다. - 그리고
@Aspect를 붙여 Aspect 역할을 할 클래스임을 나타낸다. - 클래스 내부에 참조형 메소드를 생성하여
@Pointcut("execution(~)")을 생성한다. - Advice 메소드 위
@Before("참조형 메소드명()")@After("참조형 메소드명()")@AfterReturning(pointcut="참조형 메소드명()", returning="변환데이터변수명")@AfterThrowing(pointcut="참조형 메소드명()", throwing="예외변수명")@Around("참조형 메소드명()")
- Pointcut의 execution 식과 참조형 메소드를 묶어 클래스를 만들어 클래스명.메소드명으로 호출할 수도 있다.
예시
@Service //bean 대신 객체 등록
@Aspect //Aspect 등록
public class AroundAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.naver.service..*service.*(..))")
public void myPointcut() {}
@Around("myPointcut()")
public Object aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{
//...생략
}
}
@Service //bean 대신 객체 등록
@Aspect //Aspect 등록
public class AfterReturningAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void com.naver.data..*.*(..))")
public void myPointcut() {}
@AfterReturning(pointcut="myPointcut()", returning ="returnObject")
public Object afterReturningAdvice(JoinPoint jp, Object returnObject) throws Throwable{
//...생략
}
}
Reference: